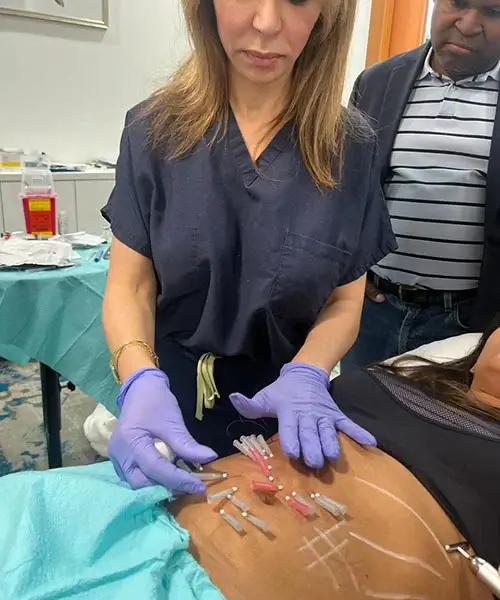
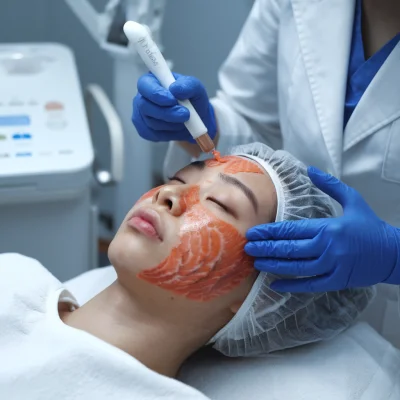
Many different aesthetic procedures can be categorized as body sculpting or body contouring procedures. Some are invasive while others are relatively low-intervention.
Patients often confuse esthetician body sculpting procedures with physician-assisted weight loss programs because they’re both led by trained medical professionals and both often have the effect of reducing patients’ weight, at least temporarily.
But these two types of treatment are very different. Here’s what you need to know about them and how to choose the right path for your personal needs.
Body Sculpting vs. Weight Loss
Body sculpting (or body contouring) describes a set of related cosmetic or aesthetic procedures supervised by trained (usually licensed and board-certified) professionals.
“Weight loss,” in simplest terms, is the act of losing weight. In a medical context, weight loss describes interventions aimed at safely and sustainably helping patients achieve and maintain healthy weight. These interventions usually begin with and remain focused on diet and exercise, sometimes in conjunction with weight loss medication, but may eventually involve more invasive surgical procedures.
What Is Body Sculpting?
Body sculpting attacks and removes fat from specific areas of the body. Because even noninvasive body contouring can have unwanted side effects, it’s important for patients to work with providers trained to perform body contouring procedures.
Examples of body sculpting include:
- Targeted surgeries, such as abdominoplasty (tummy tuck), surgical arm and butt lifts, and breast reduction surgery
- Liposuction, a less invasive surgical procedure that removes fat from specific areas of the body
- Noninvasive radio frequency treatments, which are less effective at long-term fat removal but can help with skin tightening after surgery or medically supervised weight loss
- Cryolipolysis, another noninvasive treatment that freezes fat cells under the skin, enabling the body to expel them over time
What Is Weight Loss?
Medical weight loss is a process that helps patients safely achieve a healthy weight for a long period of time, without the “bounceback” or “yo-yo” effect that can occur during unsupervised dieting-based attempts to lose weight.
Medical weight loss typically involves some combination of dietary changes, regular exercise, prescription weight loss medication, and (only if necessary) more aggressive interventions like bariatric surgery. Each course of treatment should be tailored to the individual patient and designed for a slow, steady approach — generally a few pounds per month. This allows the body to acclimate over time and reduces the risk of sudden weight gain after treatment ends.
Body Sculpting and Weight Loss: Treatment Order & Other Considerations
Many patients pursue body sculpting and weight loss treatments simultaneously or in succession.
Physician-assisted weight loss often comes first, followed by body contouring treatment once the patient is at a stable lower weight. Patients who prioritize body contouring treatments may have difficulty maintaining the “new” shape; fat cells can return to the treated areas relatively quickly. They may also be less motivated to make lifestyle changes that result in sustainable weight loss.
On the other hand, patients already at a healthy and relatively stable weight have no need for additional medical weight loss treatments. They may be ready for less invasive body contouring treatments or for more drastic interventions to attack really stubborn areas of fat.